-
Airless Spray
Airless spray is one of our application techniques for applying several different type of coatings.
Benefits:
Polymer applied coatings.
Best Used For:
Wide range of polymer coating applications.
View Details -
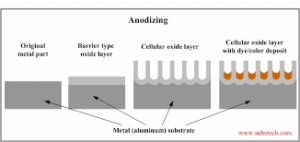
Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a decorative, durable, corrosion-resistant, anodic oxide finish.
Benefits:
Aluminum is ideally suited to anodizing, although other nonferrous metals, such as magnesium and titanium, also can be anodized.
Best Used For:
We provide anodizing to a wide variety of parts and is one of the various services that we offer.
View Details -
Combustion Wire Metallizing
In this process, various metal wire is fed into an oxygen-acetylene gas mixture. It is then in a molten state and sprayed onto the part being processed.
Benefits:
This most basic of coating techniques is limited by maximum temperature attainable and the universe of materials that can be set.
Best Used For:
Utilized to apply metal based coatings.
View Details -
Electric Arc
This process uses materials in wire form, but the heat source is the arcing of two electrically conductive wires. Material is melted and propelled on the part at a greater velocity than metallizing.
Benefits:
Higher temperatures allow for an increased source of base materials, faster rates of deposition, and improved bond and coating density.
Best Used For:
Utilized to apply metal based coatings.
View Details -
Electrostatic
Through our electrostatic systems we are able to apply: fluorocarbons, fluoropolymers, silicones, epoxies, and Teflon® industrial coatings.
Benefits:
Polymer applied coatings.
Best Used For:
Wide range of polymer coating applications.
View Details -
HVOF
In this process metal particles actually travel faster than the speed of sound, generating the best bond strengths, density and hardness of all our processes.
Benefits:
HVOF does not reach temperatures that are attainable with plasma processes so materials such as ceramicsare not processed with this technique.
Best Used For:
Utilized to apply metal based coatings.
View Details -
Laser Cladding
Laser cladding is an additive manufacturing process that utilizes a laser to metallurgically bond performance coatings to a product’s base material.
Benefits:
The process uses the laser to create a melt pool of the base material. The coating material is introduced into this melt pool in either powder or wire form.
Best Used For:
A wide range of cladding applications; including small footprint applications.
View Details -
Liquid Dispersion
Liquid dispersion is a polymer coating process technique used in a wide variety of applications.
Benefits:
Polymer applied coatings.
Best Used For:
Wide range of polymer coating applications.
View Details -
Plasma Spray
In this process we use various gasses that are ignited by an electric arc. Temperatures can rise up to 30,000° F while the part temperature remains at less than 200°F.
Benefits:
Particle velocity is greater than in the other four systems. One of the benefits of using this system is the high heat, which can process materials with high melting points (including ceramics).
Best Used For:
Utilized to apply metal and ceramic based coatings.
View Details -
Plasma Transferred Arc
We manufacture and utlize plasma transferred arc welding or cladding systems to provide wear and corrosion resistant coatings or claddings.
Benefits:
Provide a protective wear layer or rebuild parts back to original dimensional integrity.
Best Used For:
This technology is used to rebuild surfaces back to original dimensional integrity.
View Details -
Powder Coat
The powder coat process is used in many of our polmyer coating processes.
Benefits:
Polymer applied coatings.
Best Used For:
Wide range of polymer coating applications.
View Details -
Thermal Spray
Method of applying materials onto a base material by heating particles, creating a semi-molten state. Particles then propelled by high velocity onto a substrate and adhere via a mechanical bond.
Benefits:
This technique is considered the "cold method of welding", where high temperatures can be achieved in the heated pocket, while the temperature of the part itself usually remains under 200°F.
Best Used For:
Utilized to apply metal and ceramic based coatings.
View Details
Showing all 12 results